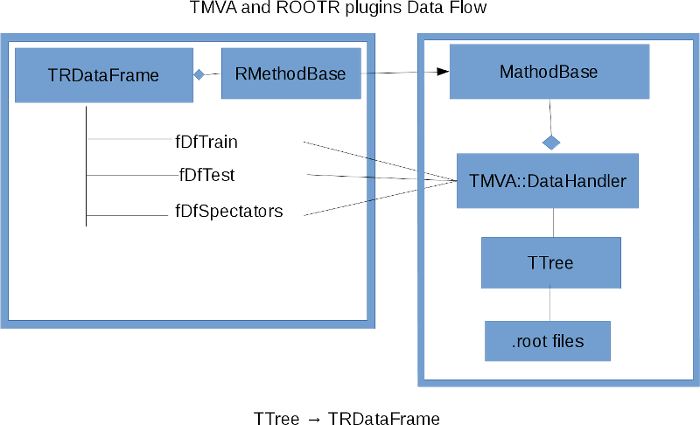
R TMVA
R TMVA

- Description
- Installation
- Boosted Decision Trees and Rule-Based Models (Package C50)
- Neural Networks in R using the Stuttgart Neural Network Simulator (Package RSNNS)
- Support Vector Machine (R package e1071)
Description
RMVA is a set of plugins for TMVA based on ROOTR that allows the use of R’s classification and regression in TMVA.
Installation
Install needed R packages, open R and in the prompt type.
install.packages(c('Rcpp','RInside','C50','ROCR','caret','RSNNS','e1071','devtools'), dependencies=TRUE)
select a mirror and install. For xgboost.
devtools::install_github('dmlc/xgboost',subdir='R-package')
Download code from git repo.
git clone https://github.com/root-mirror/root.git
To compile ROOTR lets to create a compilation directory and to activate it use cmake -Dr=ON ..
mkdir compile
cd compile
cmake -Dr=ON ..
make -j n
Where n is the number of parallel jobs to compile.
Boosted Decision Trees and Rule-Based Models (Package C50)
C50 Booking Options
Configuration options reference for MVA method: C50
C50 Booking Options
| Configuration options reference for MVA method: C50 | |||
| Option | Default Value | Predefined values | Description |
| nTrials | 1 | - | an integer specifying the number of boosting iterations. A value of one indicates that a single model is used. |
| Rules | kFALSE | - | A logical: should the tree be decomposed into a rule-based model? |
| Configuration options for C5.0Control : C50 | |||
| ControlSubset | kTRUE | - | AA logical: should the model evaluate groups of discrete predictors for splits? Note: the C5.0 command line version defaults this parameter to ‘FALSE’, meaning no attempted gropings will be evaluated during the tree growing stage. |
| ControlBands | 0 | 2-1000 | An integer between 2 and 1000. If ‘TRUE’, the model orders the rules by their affect on the error rate and groups the rules into the specified number of bands. This modifies the output so that the effect on the error rate can be seen for the groups of rules within a band. If this options is selected and ‘rules = kFALSE’, a warning is issued and ‘rules’ is changed to ‘kTRUE’. |
| ControlWinnow | kFALSE | - | A logical: should predictor winnowing (i.e feature selection) be used? |
| ControlNoGlobalPruning | kFALSE | - | A logical to toggle whether the final, global pruning step to simplify the tree. |
| ControlCF | 0.25 | - | A number in (0, 1) for the confidence factor. |
| ControlMinCases | 2 | - | An integer for the smallest number of samples that must be put in at least two of the splits. |
| ControlFuzzyThreshold | kFALSE | - | A logical toggle to evaluate possible advanced splits of the data. See Quinlan (1993) for details and examples. |
| ControlSample | 0 | - | A value between (0, .999) that specifies the random proportion of the data should be used to train the model. By default, all the samples are used for model training. Samples not used for training are used to evaluate the accuracy of the model in the printed output. |
| ControlSeed | ? | - | An integer for the random number seed within the C code. |
| ControlEarlyStopping | kTRUE | - | A logical to toggle whether the internal method for stopping boosting should be used. |
Example Booking C50 to generate Rule Based Model
factory->BookMethod( loader, TMVA::Types::kC50, "C50",
"!H:NTrials=10:Rules=kTRUE:ControlSubSet=kFALSE:ControlBands=10:ControlWinnow=kFALSE:ControlNoGlobalPruning=kTRUE:ControlCF=0.25:ControlMinCases=2:ControlFuzzyThreshold=kTRUE:ControlSample=0:ControlEarlyStopping=kTRUE:!V" );
NOTE: Options Rules=kTRUE and to Control the bands use ControlBands
Example Booking C50 to generate Boosted Decision Trees Model
factory->BookMethod(loader, TMVA::Types::kC50, "C50",
"!H:NTrials=10:Rules=kFALSE:ControlSubSet=kFALSE:ControlWinnow=kFALSE:ControlNoGlobalPruning=kTRUE:ControlCF=0.25:ControlMinCases=2:ControlFuzzyThreshold=kTRUE:ControlSample=0:ControlEarlyStopping=kTRUE:!V" );
NOTE: Options Rules=kFALSE or remove this option because by default is Boosted Decision Tree Model and remove ControlBands option that is only for Rule Based model.
C50 Output
RMVA produces output in stdout, in the .root file indicate in TMVA::Factory and in a directory called C50. in the directory you can find at the moment a dir called plots with ROC curve, but It will have a .RData file with all R’s objects used for ROOTR if you want to reproduce the procedures again or try other stuff.
C50 Plot
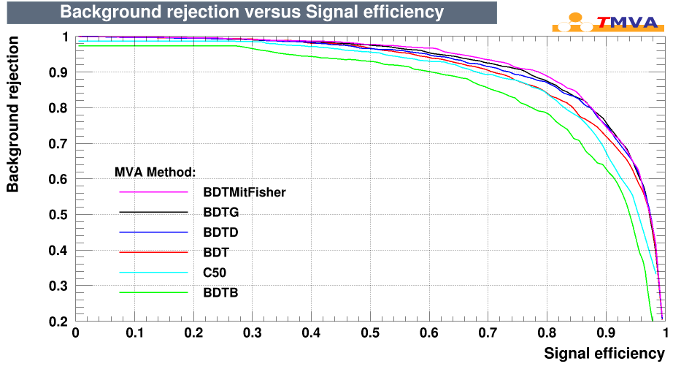
C50 Example
#include "TFile.h"
#include "TTree.h"
#include "TString.h"
#include "TMVA/Factory.h"
#include "TMVA/Tools.h"
#include<TMVA/MethodC50.h>
void c50()
{
// This loads the library
TMVA::Tools::Instance();
// Create a ROOT output file where TMVA will store ntuples, histograms, etc.
TString outfileName( "TMVA.root" );
TFile* outputFile = TFile::Open( outfileName, "RECREATE" );
TMVA::Factory *factory = new TMVA::Factory( "RMVAClassification", outputFile,
"!V:!Silent:Color:DrawProgressBar:Transformations=I;D;P;G,D:AnalysisType=Classification" );
TMVA::DataLoader *loader=new TMVA::DataLoader("dataset");
// Define the input variables that shall be used for the MVA training
loader->AddVariable( "myvar1 := var1+var2", 'F' );
loader->AddVariable( "myvar2 := var1-var2", "Expression 2", "", 'F' );
loader->AddVariable( "var3", "Variable 3", "units", 'F' );
loader->AddVariable( "var4", "Variable 4", "units", 'F' );
// You can add so-called "Spectator variables", which are not used in the MVA training,
// but will appear in the final "TestTree" produced by TMVA. This TestTree will contain the
// input variables, the response values of all trained MVAs, and the spectator variables
loader->AddSpectator( "spec1 := var1*2", "Spectator 1", "units", 'F' );
loader->AddSpectator( "spec2 := var1*3", "Spectator 2", "units", 'F' );
// Read training and test data
TString fname = "./tmva_class_example.root";
if (gSystem->AccessPathName( fname )) // file does not exist in local directory
gSystem->Exec("curl -O http://root.cern.ch/files/tmva_class_example.root");
TFile *input = TFile::Open( fname );
std::cout << "--- TMVAClassification : Using input file: " << input->GetName() << std::endl;
// --- Register the training and test trees
TTree *tsignal = (TTree*)input->Get("TreeS");
TTree *tbackground = (TTree*)input->Get("TreeB");
// global event weights per tree (see below for setting event-wise weights)
Double_t signalWeight = 1.0;
Double_t backgroundWeight = 1.0;
// You can add an arbitrary number of signal or background trees
loader->AddSignalTree ( tsignal, signalWeight );
loader->AddBackgroundTree( tbackground, backgroundWeight );
// Set individual event weights (the variables must exist in the original TTree)
// for signal : factory->SetSignalWeightExpression ("weight1*weight2");
// for background: factory->SetBackgroundWeightExpression("weight1*weight2");
loader->SetBackgroundWeightExpression( "weight" );
// Apply additional cuts on the signal and background samples (can be different)
TCut mycuts = ""; // for example: TCut mycuts = "abs(var1)<0.5 && abs(var2-0.5)<1";
TCut mycutb = ""; // for example: TCut mycutb = "abs(var1)<0.5";
// Tell the factory how to use the training and testing events
// If no numbers of events are given, half of the events in the tree are used
// for training, and the other half for testing:
// factory->PrepareTrainingAndTestTree( mycut, "SplitMode=random:!V" );
// To also specify the number of testing events, use:
// factory->PrepareTrainingAndTestTree( mycut,
// "NSigTrain=3000:NBkgTrain=3000:NSigTest=3000:NBkgTest=3000:SplitMode=Random:!V" );
loader->PrepareTrainingAndTestTree( mycuts, mycutb,
"nTrain_Signal=0:nTrain_Background=0:SplitMode=Random:NormMode=NumEvents:!V" );
// Boosted Decision Trees
// Gradient Boost
factory->BookMethod(loader, TMVA::Types::kBDT, "BDTG",
"!H:!V:NTrees=1000:MinNodeSize=2.5%:BoostType=Grad:Shrinkage=0.10:UseBaggedBoost:BaggedSampleFraction=0.5:nCuts=20:MaxDepth=2" );
// Adaptive Boost
factory->BookMethod(loader, TMVA::Types::kBDT, "BDT",
"!H:!V:NTrees=850:MinNodeSize=2.5%:MaxDepth=3:BoostType=AdaBoost:AdaBoostBeta=0.5:UseBaggedBoost:BaggedSampleFraction=0.5:SeparationType=GiniIndex:nCuts=20" );
// Bagging
factory->BookMethod(loader, TMVA::Types::kBDT, "BDTB",
"!H:!V:NTrees=400:BoostType=Bagging:SeparationType=GiniIndex:nCuts=20" );
// Decorrelation + Adaptive Boost
factory->BookMethod(loader, TMVA::Types::kBDT, "BDTD",
"!H:!V:NTrees=400:MinNodeSize=5%:MaxDepth=3:BoostType=AdaBoost:SeparationType=GiniIndex:nCuts=20:VarTransform=Decorrelate" );
// Allow Using Fisher discriminant in node splitting for (strong) linearly correlated variables
factory->BookMethod(loader, TMVA::Types::kBDT, "BDTMitFisher",
"!H:!V:NTrees=50:MinNodeSize=2.5%:UseFisherCuts:MaxDepth=3:BoostType=AdaBoost:AdaBoostBeta=0.5:SeparationType=GiniIndex:nCuts=20" );
factory->BookMethod(loader, TMVA::Types::kC50, "C50",
"!H:NTrials=10:Rules=kFALSE:ControlSubSet=kFALSE:ControlNoGlobalPruning=kFALSE:ControlCF=0.25:ControlMinCases=2:ControlFuzzyThreshold=kTRUE:ControlSample=0:ControlEarlyStopping=kTRUE:!V" );
// Train MVAs using the set of training events
factory->TrainAllMethods();
// ---- Evaluate all MVAs using the set of test events
factory->TestAllMethods();
// ----- Evaluate and compare performance of all configured MVAs
factory->EvaluateAllMethods();
// --------------------------------------------------------------
// Save the output
outputFile->Close();
std::cout << "==> Wrote root file: " << outputFile->GetName() << std::endl;
std::cout << "==> TMVAClassification is done!" << std::endl;
delete factory;
delete loader;
}
Neural Networks in R using the Stuttgart Neural Network Simulator (Package RSNNS)
The Stuttgart Neural Network Simulator (SNNS) is a library containing many standard implementations of neural networks. This package wraps the SNNS functionality to make it available from within R. Using the RSNNS low-level interface, all of the algorithmic functionality and flexibility of SNNS can be accessed. Furthermore, the package contains a convenient high-level interface, so that the most common neural network topologies and learning algorithms integrate seamlessly into R.
RSNNS/MLP Create and train a multi-layer perceptron
MLPs are fully connected feedforward networks, and probably the most common network architecture in use. Training is usually performed by error backpropagation or a related procedure.
RSNNS/MLP Booking Options
| Configuration options reference for MVA method: RSNNS/MLP | |||
| Option | Default Value | Predefined values | Description |
| Size | c(5) | - | (R's vector type given in string) with the number of units in the hidden layer(s) |
| Maxit | 100 | - | maximum of iterations to learn |
| InitFunc | Randomize_Weights | Randomize_Weights ART1_Weights ART2_Weights ARTMAP_Weights CC_Weights ClippHebb CPN_Weights_v3.2 CPN_Weights_v3.3 CPN_Rand_Pat DLVQ_Weights Hebb Hebb_Fixed_Act JE_Weights Kohonen_Rand_Pat Kohonen_Weights_v3.2 Kohonen_Const PseudoInv Random_Weights_Perc RBF_Weights RBF_Weights_Kohonen RBF_Weights_Redo RM_Random_Weights ENZO_noinit | the initialization function to use |
| InitFuncParams | c(-0.3, 0.3) | - | (R's vector type given in string) the parameters for the initialization function |
| LearnFunc | Std_Backpropagation | Std_Backpropagation BackpropBatch BackpropChunk BackpropClassJogChunk BackpropMomentum BackpropWeightDecay TimeDelayBackprop Quickprop Rprop RpropMAP BPTT CC TACOMA BBPTT QPTT JE_BP JE_BP_Momentum JE_Quickprop JE_Rprop Monte-Carlo SCG Sim_Ann_SS Sim_Ann_WTA Sim_Ann_WWTA | the learning function to use |
| LearnFuncParams | c(0.2, 0) | - | (R's vector type given in string) the parameters for the learning function e.g. ‘Std_Backpropagation’, ‘BackpropBatch’ have two parameters, the learning rate and the maximum output difference. The learning rate is usually a value between 0.1 and 1. It specifies the gradient descent step width. The maximum difference defines, how much difference between output and target value is treated as zero error, and not backpropagated. This parameter is used to prevent overtraining. For a complete list of the parameters of all the learning functions, see the SNNS User Manual, pp. 67. |
| UpdateFunc | Topological_Order | Topological_Order ART1_Stable ART1_Synchronous ART2_Stable ART2_Synchronous ARTMAP_Stable ARTMAP_Synchronous Auto_Synchronous BAM_Order BPTT_Order CC_Order CounterPropagation Dynamic_LVQ Hopfield_Fixed_Act Hopfield_Synchronous JE_Order JE_Special Kohonen_Order Random_Order Random_Permutation Serial_Order Synchonous_Order TimeDelay_Order ENZO_prop | the update function to use |
| UpdateFuncParams | c(0) | - | the parameters for the update function |
| HiddenActFunc | Act_Logistic | Act_Logistic Act_Elliott Act_BSB Act_TanH Act_TanHPlusBias Act_TanH_Xdiv2 Act_Perceptron Act_Signum Act_Signum0 Act_Softmax Act_StepFunc Act_HystStep Act_BAM Logistic_notInhibit Act_MinOutPlusWeight Act_Identity Act_IdentityPlusBias Act_LogisticTbl Act_RBF_Gaussian Act_RBF_MultiQuadratic Act_RBF_ThinPlateSpline Act_less_than_0 Act_at_most_0 Act_at_least_1 Act_at_least_2 Act_exactly_1 Act_Product Act_ART1_NC Act_ART2_Identity Act_ART2_NormP Act_ART2_NormV Act_ART2_NormW Act_ART2_NormIP Act_ART2_Rec Act_ART2_Rst Act_ARTMAP_NCa Act_ARTMAP_NCb Act_ARTMAP_DRho Act_LogSym Act_TD_Logistic Act_TD_Elliott Act_Euclid Act_Component Act_RM Act_TACOMA Act_CC_Thresh Act_Sinus Act_Exponential | the activation function of all hidden units |
| ShufflePatterns | kTRUE | - | should the patterns be shuffled? |
| LinOut | kFALSE | - | sets the activation function of the output units to linear or logistic |
| PruneFunc | NULL | MagPruning OptimalBrainDamage OptimalBrainSurgeon Skeletonization Noncontributing_Units None Binary Inverse Clip LinearScale Norm Threshold | the pruning function to use |
| PruneFuncParams | NULL | - | the parameters for the pruning function. |
Example Booking RSNNS/MLP Model
factory->BookMethod(loader, TMVA::Types::kRSNNS, "RMLP","!H:VarTransform=N:Size=c(5):Maxit=800:InitFunc=Randomize_Weights:LearnFunc=Std_Backpropagation:LearnFuncParams=c(0.2,0):!V" );
RSNNS/MLP Plot
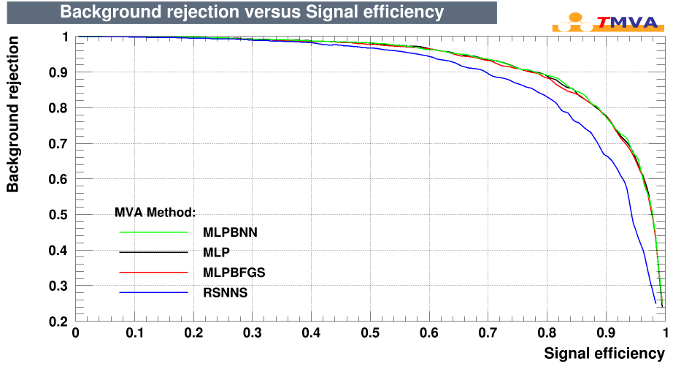
Support Vector Machine (R package e1071)
Misc Functions of the Department of Statistics (e1071), TU Wien Functions for latent class analysis, short time Fourier transform, fuzzy clustering, support vector machines, shortest path computation, bagged clustering, naive Bayes classifier, …
RSVM (R Support Vector Machines)
svm is used to train a support vector machine. It can be used to carry out general regression and classification (of nu and epsilon-type), as well as density-estimation.
e1071/RSVM Booking Options
e1071/RSVM Booking Options
| Option | Default Value | Predefined values | Description |
| Scale | kTRUE | - | A logical vector indicating the variables to be scaled. If ‘scale’ is of length 1, the value is recycled as many times as needed. Per default, data are scaled internally (both ‘x’ and ‘y’ variables) to zero mean and unit variance. The center and scale values are returned and used for later predictions. |
| Type | C-classification | C-classification nu-classification one-classification eps-regression nu-regression | ‘svm’ can be used as a classification machine, as a regression machine, or for novelty detection. Depending of whether ‘y’ is a factor or not, the default setting for ‘type’ is ‘C-classification’ or ‘eps-regression’, respectively, but may be overwritten by setting an explicit value. |
| Kernel | radial | radial linear polynomial sigmoid | the kernel used in training and predicting. You might consider changing some of the following parameters, depending on the kernel type. |
| Degree | 3 | - | parameter needed for kernel of type ‘polynomial’ |
| Gamma | default: 1/(data dimension) | - | parameter needed for all kernels except ‘linear’ |
| Coef0 | 0 | - | parameter needed for kernels of type ‘polynomial’ and ‘sigmoid’ |
| Cost | 1 | - | cost of constraints violation (default: 1)-it is the ‘C’-constant of the regularization term in the Lagrange formulation. |
| Nu | 0.5 | - | parameter needed for ‘nu-classification’, ‘nu-regression’, and ‘one-classification’ |
| CacheSize | 40 | - | cache memory in MB (default 40) |
| Tolerance | 0.001 | - | tolerance of termination criterion (default: 0.001) |
| Epsilon | 0.1 | - | epsilon in the insensitive-loss function (default: 0.1) |
| Shrinking | kTRUE | - | option whether to use the shrinking-heuristics |
| Cross | 0 | - | if a integer value k>0 is specified, a k-fold cross validation on the training data is performed to assess the quality of the model: the accuracy rate for classification and the Mean Squared Error for regression |
| Fitted | kTRUE | - | logical indicating whether the fitted values should be computed and included in the model or not (default: ‘TRUE’) |
| Probability | kFALSE | - | logical indicating whether the model should allow for probability predictions. |
Example Booking RSVM Model
factory->BookMethod(loader, TMVA::Types::kRSVM, "RSVM","!H:Kernel=linear:Type=C-classification:VarTransform=Norm:Probability=kTRUE:Tolerance=0.001:!V" );
e1071/RSVM Plot
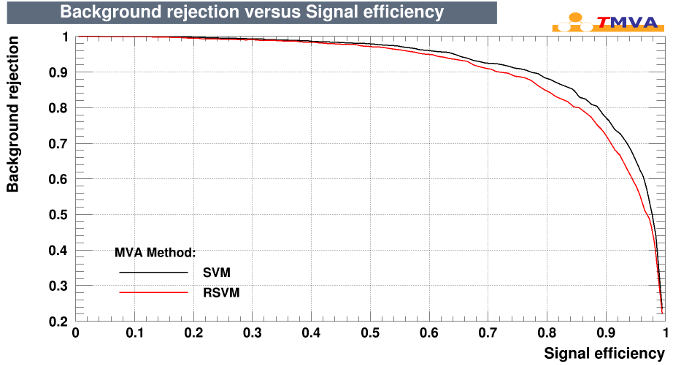
eXtreme Gradient Boost (R package xgboost)
An optimized general purpose gradient boosting library. The library is parallelized, and also provides an optimized distributed version.
It implements machine learning algorithms under the Gradient Boosting framework, including Generalized Linear Model (GLM) and Gradient Boosted Decision Trees (GBDT). XGBoost can also be distributed and scale to Terascale data
XGBoost is part of Distributed Machine Learning Common projects.
RXGB Booking Options
| Configuration options reference for MVA method: RXGB | |||
| Option | Default Value | Predefined values | Description |
| NRounds | 10 | - | an integer specifying the number of boosting iterations. |
| Eta | 0.3 | - | Step size shrinkage used in update to prevents overfitting. After each boosting step, we can directly get the weights of new features. and eta actually shrinks the feature weights to make the boosting process more conservative. |
| MaxDepth | 6 | - | Maximum depth of the tree |
Booking Options Example
factory->BookMethod(TMVA::Types::kRXGB,"RXGB","!V:NRounds=80:MaxDepth=2:Eta=1");
RXGB Output
Evaluation results ranked by best signal efficiency and purity (area)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
MVA Signal efficiency at bkg eff.(error): | Sepa- Signifi-
Method: @B=0.01 @B=0.10 @B=0.30 ROC-integ. | ration: cance:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
RXGB : 0.264(08) 0.660(08) 0.866(06) 0.876 | 0.433 1.169
C50 : 0.087(05) 0.440(09) 0.861(06) 0.844 | 0.391 1.097
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------



